A blockchain node is a crucial element of any decentralized network, responsible for storing, verifying, and distributing blockchain data. Without nodes, cryptocurrencies and smart contracts wouldn’t function, as they enable transaction validation and network security. One of the most efficient ways to interact with a blockchain is through RPC nodes and endpoints, which allow developers, researchers, and businesses to send and receive data seamlessly.
Understanding how RPC nodes work is essential for anyone involved in Web3 development. This guide will explore the role of RPC nodes, their practical applications, and how NOWNodes provides reliable infrastructure for blockchain interaction. Let’s dive into the details and see how you can leverage nodes for your projects.
What Is RPC in Web3?
RPC stands for Remote Procedure Call. In the context of blockchain nodes, particularly in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, RPC allows you to interact with a node remotely, as the name suggests. Here’s a simple rundown of the pivotal points:
- Remote: you can access the node from a different computer or location. You don’t have to be physically present where the node is running.
- Procedure Call: You can call specific functions or procedures that the node provides. These functions can vary depending on the network protocol and the capabilities of the node software.
- Blockchain Nodes: Nodes are essentially computers running software that enables them to participate in the network. They store a copy of the blockchain and can validate transactions and blocks.
So, when you use RPC nodes, you’re essentially sending commands or requests to the node from a remote location to perform certain actions like sending transactions, querying information about the blockchain, or even configuring the node itself.
What Is the Difference Between RPC Endpoint and Node?
RPC endpoints are specific addresses or URLs through which you can access the Remote Procedure Call functionality provided by a blockchain node. These endpoints act as entry points for making RPC requests to interact with the node’s services and functionalities remotely.
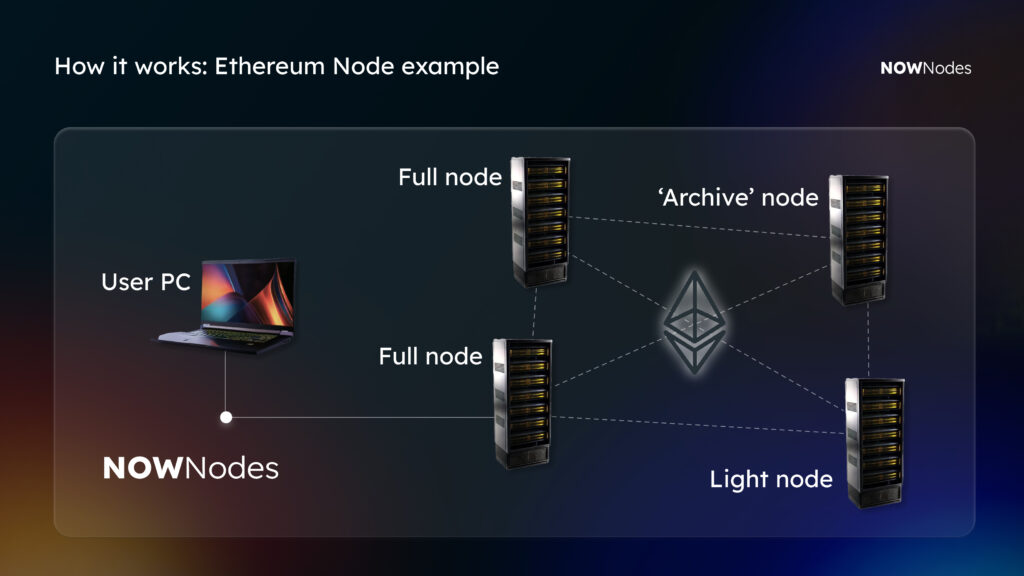
In other words, an RPC node is the actual server (full, light, or archive node) that processes these requests, validates transactions, and returns blockchain data. In short: the node is the engine, while the endpoint is the doorway to it.
What are the Nuances of RPC Nodes?
To understand RPC Nodes better, you need to look into the different types and what makes each one unique. RPC nodes come in different types, each serving specific purposes:
- Dedicated nodes: These are like private servers offering top-notch performance.
- Private nodes: They limit access to certain users or applications for added security.
- Shared nodes: These are like shared servers, offering a more budget-friendly option for multiple users.
RPC nodes can also be categorized as full nodes, light nodes, or archive nodes, depending on how much blockchain data they store and provide. This flexibility is crucial for developers choosing the right infrastructure.
Diverse Usage of RPC Nodes in Web3
For many users, RPC nodes are essential, although their operation is mostly automated. Often, the inner workings of these nodes remain unknown, especially when performing routine tasks in the cryptocurrency landscape. Here are some simple examples of RPC Nodes in action:
- Sending a Transaction: Imagine you have a cryptocurrency wallet application on your phone. When you initiate a transfer of cryptocurrency from your wallet to another person’s wallet, your wallet app sends an RPC request to a node on the network. This RPC request contains information about the transaction, such as the recipient’s address and the amount of cryptocurrency to send.
- Querying Blockchain Information: Let’s say you want to check the balance of your cryptocurrency wallet or view the details of a particular transaction. You can send an RPC request to a node on the network asking for this information.
- Executing a Smart Contract: For example, if you have a decentralized application (dApp) that allows users to trade digital assets, you can send RPC requests to the Ethereum network to execute functions in your smart contract, such as buying or selling assets.
Who Can Use RPC Nodes?
RPC nodes provide a gateway for various users to interact with blockchain networks. While everyday users unknowingly rely on RPC when sending crypto, developers and researchers actively utilize them for more advanced functions.
- Developers building dApps or DeFi platforms use RPC to query blockchain data and execute smart contracts. For instance, a trading dApp can interact with Ethereum smart contracts via RPC to enable asset transactions.
- Blockchain researchers leverage RPC to analyze transaction histories, contract states, and other on-chain data for insights.
In short, RPC nodes bridge users, developers, and researchers with blockchain networks, ensuring seamless interaction and data access.
Start Your RPC Journey With NOWNodes
For those who seek development support in order to maintain the dApp or DeFi platform, NOWNodes comes right into the place. NOWNodes provides developers with access to a network of dependable RPC Nodes across multiple networks. This approach simplifies the process of building and deploying blockchain-based applications.
NOWNodes offers a user-friendly interface and flexible pricing plans to suit your needs:
- Sign up for an account and verify it by email. No KYC required.
- Choose a tariff plan. There are a variety of plans that fit any development needs, including a START FREE plan!
- Explore the available RPC Nodes for their desired networks.
- Create an API key. On the “DASHBOARD” page find and click the “ADD API KEY” button.
- Use the provided endpoint and the methods from the “DOCS” page to interact with the blockchain.
- Retrieve data.
- And execute transactions seamlessly.
With NOWNodes by your side, you can focus on unleashing your creativity and driving innovation in decentralized development.
Conclusion
To sum up, RPC nodes and RPC endpoints are essential for seamless interaction within decentralized networks. While RPC endpoints provide the access points (URLs) for communication, RPC nodes are the actual servers that process blockchain data, validate transactions, and execute smart contracts.
From dedicated nodes offering exclusive resources to shared nodes providing cost-effective solutions, RPC technology enhances flexibility and efficiency in blockchain operations. Developers building dApps, entrepreneurs exploring DeFi, and researchers analyzing blockchain data all rely on RPC nodes to drive innovation in 2026 and beyond.